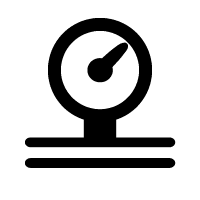
SOLVED: SNITCH expression Mus- scalar character vector Pa, convert desired unit %the pressure switch case (strcomp(b, 'Pa' ) ) P=p; case (strcomp(b, 'psi )) P-p/6894.75729; case (strcomp(b, atm' ) ) P-p/101325; otherwise
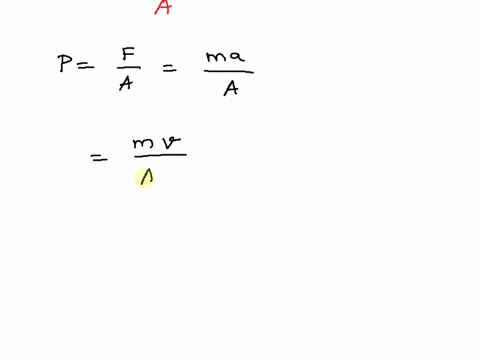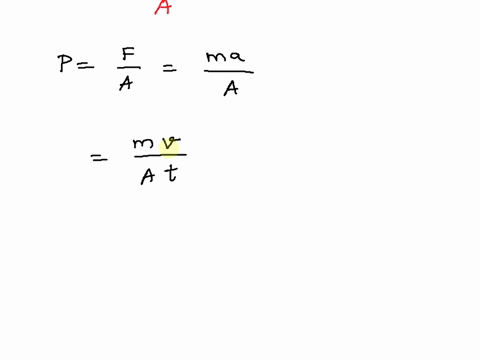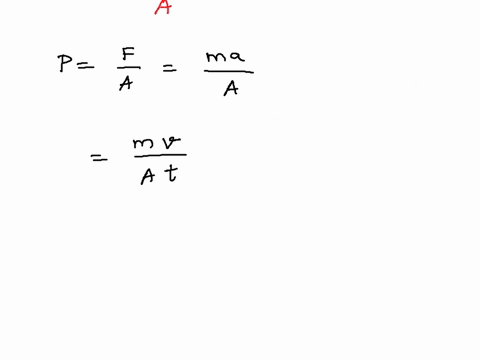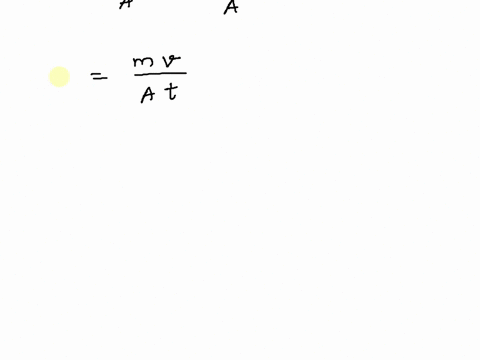
SOLVED: SNITCH expression Mus- scalar character vector Pa, convert desired unit %the pressure switch case (strcomp(b, 'Pa' ) ) P=p; case (strcomp(b, 'psi )) P-p/6894.75729; case (strcomp(b, atm' ) ) P-p/101325; otherwise
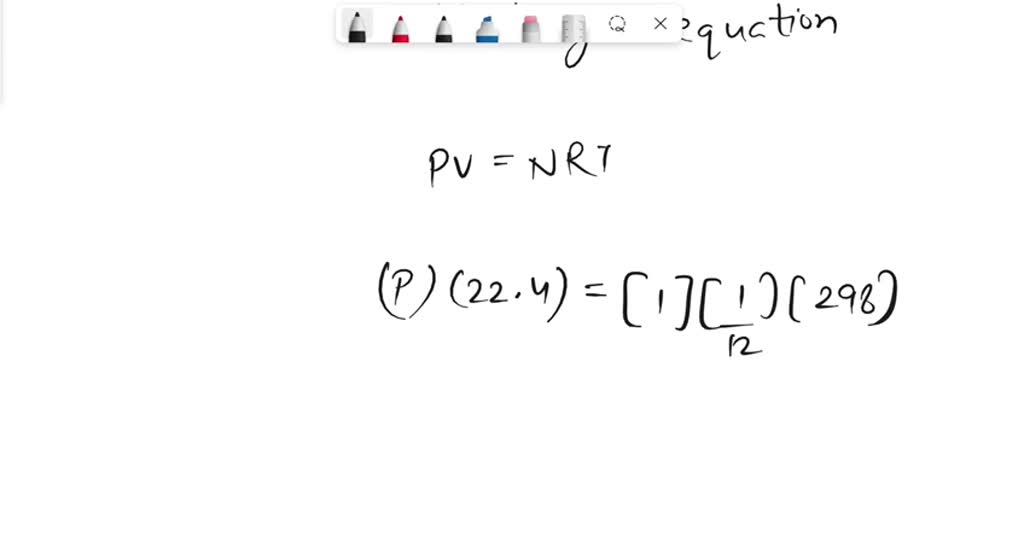
SOLVED: SNITCH expression Mus- scalar character vector Pa, convert desired unit %the pressure switch case (strcomp(b, 'Pa' ) ) P=p; case (strcomp(b, 'psi )) P-p/6894.75729; case (strcomp(b, atm' ) ) P-p/101325; otherwise
Chapter 14 Fluid In this chapter we will explore the behavior of fluids. In particular we will study the following: Static fluid
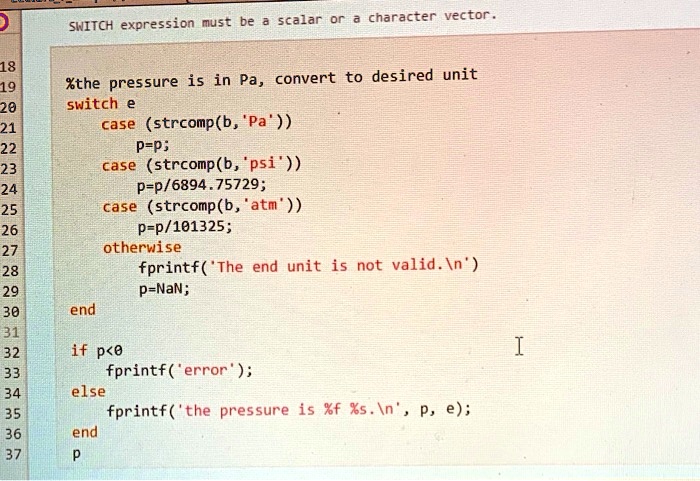
SOLVED: SNITCH expression Mus- scalar character vector Pa, convert desired unit %the pressure switch case (strcomp(b, 'Pa' ) ) P=p; case (strcomp(b, 'psi )) P-p/6894.75729; case (strcomp(b, atm' ) ) P-p/101325; otherwise